Output Settings#
The user can control several aspects of the generated code. The options can be accessed via the hamburger icon ≡ in the top right corner of the Python API Recording dialog.
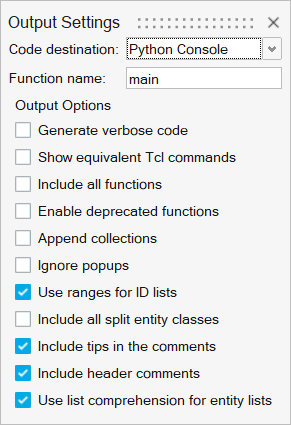
Figure 1. Output settings.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Code destination |
Defines where the generated code is output. Valid options are Python Console, Python File, and Pulse Task. |
Function name |
Defines the name of the Python function. |
Generate verbose code |
Expands the code by creating individual variables for every argument. |
Show equivalent Tcl commands |
Includes equivalent Tcl commands as comments. |
Include all functions |
Includes view, undo/redo, and similar functions. |
Enable deprecated functions |
Creates a debug model object that provides access to the deprecated functions. |
Append collections |
Appends collections when creating collections by attached/adjacent. |
Ignore popups |
Inserts model.hm_answernext(“yes”) before functions that can trigger a popup. |
Use ranges for ID lists |
Compresses full ID lists using range function. |
Include all split entity classes |
Generalizes the code to act on all split entity classes. |
Include tips in the comments |
Includes tips about available options in the comments. |
Include header comments |
Includes comments at the top of the code with the information about HyperMesh version, model file, solver interface, data, time, and username. |
Use list comprehension for entity lists |
Compresses full list of entity objects using list comprehension. |
The code destination option Pulse Task lets the user automatically generate a Pulse Task from the recorded code. It requires a Pulse installation which is used to generate the task JSON files and to output them into the Pulse Library. The function arguments are recognized and defined as Task inputs.
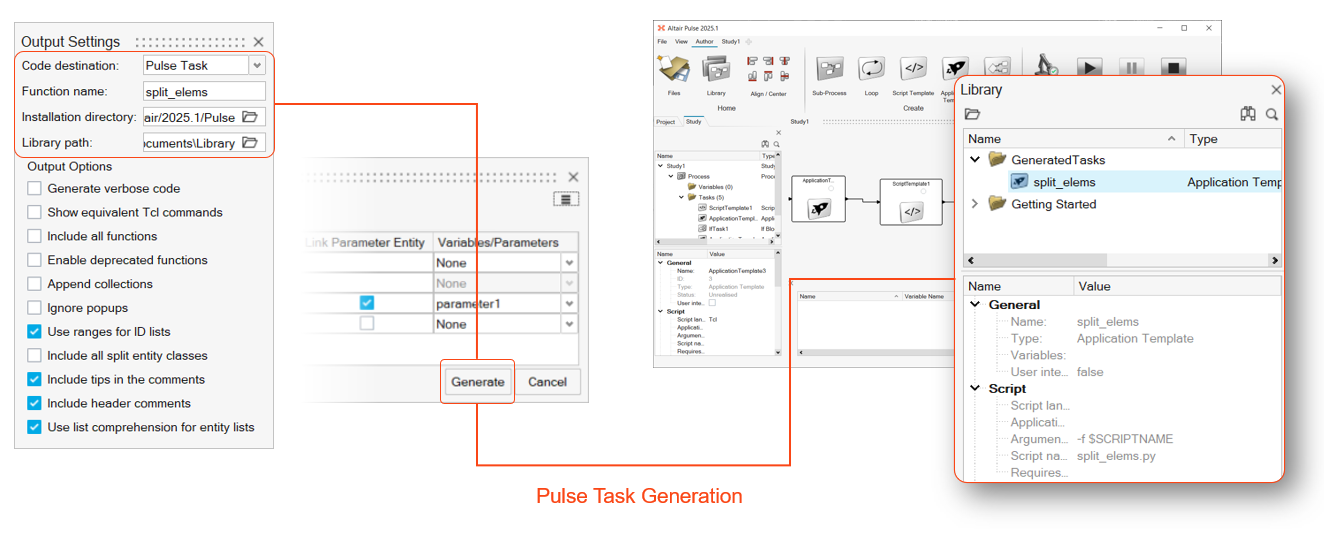
Figure 2. Generating a Pulse Task.
The following code snippets demonstrate how various output settings impact the generated code:
Generate verbose code
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[80, 82, 84, 90, 103, 105, 107, 113]))
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=0)
ids = [80, 82, 84, 90, 103, 105, 107, 113]
filterByEnumeration = hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=ids)
collection = hm.Collection(model, filterByEnumeration)
size = 0
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=size)
Show equivalent Tcl commands
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[17, 18, 19, 20]))
model.maskentitymark(collection=collection, flag=0)
# [TCL]: *createmark elements 1 17-20
# [TCL]: *maskentitymark elements 1 0
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[17, 18, 19, 20]))
model.maskentitymark(collection=collection, flag=0)
Include all functions
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[35, 36, 54, 56, 77, 78, 101, 249]))
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=0)
model.rotateabout(overridedefault=1, x=865, y=200, z=475)
model.viewset(a00=-0.161329937, a01=-0.986833866, a02=-0.0114705461, a03=0, a10=-0.553105123, a11=0.100036611, a12=-0.827083671, a13=0, a20=0.817341651, a21=-0.127088938, a22=-0.561961767, a23=0, a30=425.411852, a31=23.7688757, a32=333.19761, a33=1, minx=-92.2937276, miny=-1003.27125, maxx=1200.87036, maxy=-693.592482)
model.startnotehistorystate(name="Reverse Normals")
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[35, 36, 54, 56, 77, 78, 101, 249]))
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=0)
model.endnotehistorystate(name="Reverse Normals")
Enable deprecated functions
import hm
import hm.entities as ent
model = hm.Model()
def main():
component = ent.Component(model, 1)
propertyid = ent.Property(model, 1)
component.propertyid = propertyid
component.materialid = None
components_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Component, ids=[component.id]))
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByCollection(ent.Element, ent.Component), components_collection)
# [ERROR]: model.propertyupdate(collection=collection, property_name="property1")
import hm
import hm.entities as ent
from hm.mdi import apis
model = apis.HmModelDebug()
def main():
component = ent.Component(model, 1)
propertyid = ent.Property(model, 1)
component.propertyid = propertyid
component.materialid = None
components_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Component, ids=[component.id]))
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByCollection(ent.Element, ent.Component), components_collection)
model.propertyupdate(collection=collection, property_name="property1")
Append collections
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[78]))
collection_1 = hm.CollectionByAdjacent(model, collection)
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection_1, size=0)
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[78]))
collection = hm.CollectionByAdjacent(model, collection)
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=0)
Ignore popups
Use ranges for ID lists
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82]))
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=0)
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[*range(77,83)]))
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=0)
Inlcude all split entity classes
loadforce_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadForce, ids=[1]))
loadforce_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
loadforce_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadForce, ids=[1]))
loadforce_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
loadmoment_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadMoment, ids=hm.hwUIntList([])))
loadmoment_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
loadconstraint_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadConstraint, ids=hm.hwUIntList([])))
loadconstraint_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
loadpressure_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadPressure, ids=hm.hwUIntList([])))
loadpressure_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
loadtemperature_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadTemperature, ids=hm.hwUIntList([])))
loadtemperature_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
loadflux_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadFlux, ids=hm.hwUIntList([])))
loadflux_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
loadvelocity_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadVelocity, ids=hm.hwUIntList([])))
loadvelocity_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
loadacceleration_collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.LoadAcceleration, ids=hm.hwUIntList([])))
loadacceleration_collection.set_items('magnitude', 100)
Include tips in the comments
model.readfile(filename="C:/Users/Temp/my_model.hm", load_cad_geometry_as_graphics=0)
model.deletemodel()
# [TIP]: Command triggers popup window. Enable 'Ignore popups' to ignore it when running the script.
model.readfile(filename="C:/Users/Temp/my_model.hm", load_cad_geometry_as_graphics=0)
# [TIP]: Command triggers popup window. Enable 'Ignore popups' to ignore it when running the script.
model.deletemodel()
Include header comments
import hm
import hm.entities as ent
model = hm.Model()
def main():
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[81, 82, 83, 84]))
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=0)
# HyperMesh Python API Code Generator
# HyperMesh Version: 2025.1
# Model File: C:/Users/Temp/my_model.hm
# Solver Interface: OptiStruct
# Date: April 02, 2025
# Time: 13:27:47
# Author: username
import hm
import hm.entities as ent
model = hm.Model()
def main():
collection = hm.Collection(model, hm.FilterByEnumeration(ent.Element, ids=[81, 82, 83, 84]))
model.normalsreverse(collection=collection, size=0)
Use list comprehension for entity lists
list = [ent.Node(model, 114), ent.Node(model, 118), ent.Node(model, 119), ent.Node(model, 138)]
direction_vector = [0.999402583,0.0343760811,0.00357038225]
model.dragnodestoformsurface(list=list, direction_vector=direction_vector, distance=40)
list = [ent.Node(model, id) for id in [114, 118, 119, 138]]
direction_vector = [0.999402583,0.0343760811,0.00357038225]
model.dragnodestoformsurface(list=list, direction_vector=direction_vector, distance=40)